Table of Contents
- Overview
- Glossary
- Installation
- Tutorials
- License Operations
- Scenario Steps
- Advanced
- Application
- Screen Data
- Verification
- Clipboard
- Comparison
- Culture
- Data Source
- Date Time
- Driver
- Excel
- FTP
- File
- Flow Control
- Folder
- Format and Conversion
- Keyboard
- Loops
- Math
- Random
- Regex
- Screen
- System
- Text
- User Interface
- Windows Account Information
- Expression Development
- Embedded Development Environment
- Voodoo Connect
- Cross-Browser Scripting (CBS)
- Chrome Extension
- Firefox Extension
- Notification Center
- Unified Console
- Wrapper Libraries
- Database
- Troubleshooting
- 3rd Party Tool
- General Information
- Region
- Interface Control Manager Parameters
- Time Settings
- Scenario Flow
- On Success
- On Fail
- Let’s illustrate
- Command
Database: Run SQL Command
Data Access Component Usage Video
This is the step that performs the process of sending a SQL Command to the connected database via VooDoo Studio.
You can follow the image below to reach the database steps.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of application execution step. (Compulsory) |
| Description | The description of application execution step. (Not Compulsory) |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Related Flow Image | The using image during this step. (Compulsory) |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
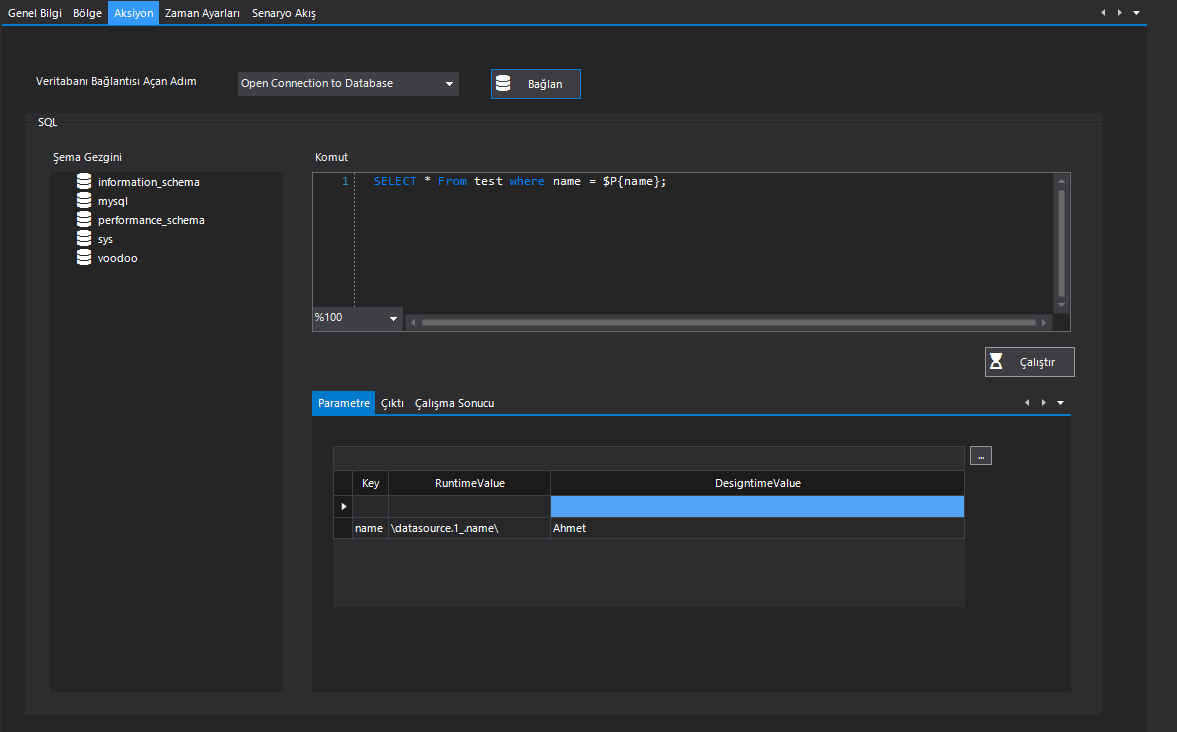
| Open Connection Step | This is the parameter that defines the step that creates the database connection. Note: Do not forget to press the “Connect” button to make the connection to the relevant database. |
| SQL: Schema Explorer | This is the Schema Explorer area where you can access the schemas in the database after connection with the database. |
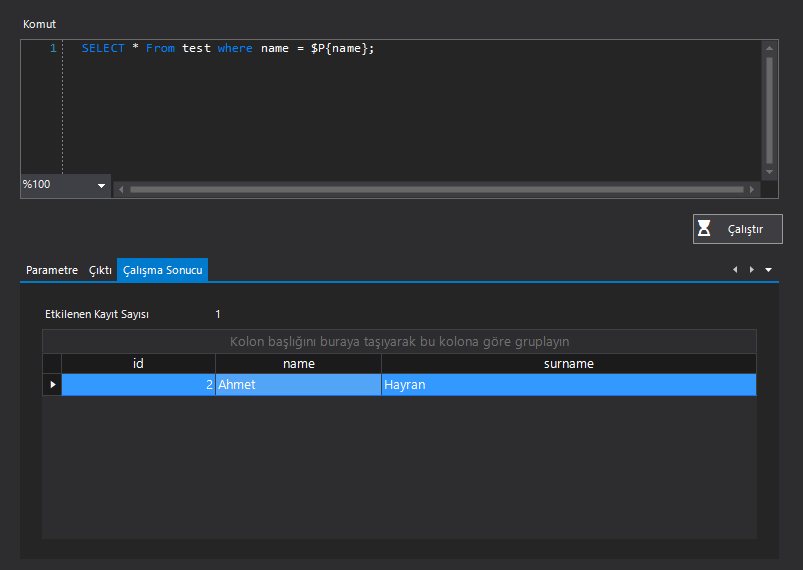
| SQL: Command | After the connection with the database, it is the Command field where you can send SQL Commands to the database. Note: After writing the SQL command for the relevant database, Don’t forget to press the “Run” button. |
| SQL: Parameter | It is the Parameter data returned from the database after the database command is sent. Key: It is the key field name parameter of the data source manipulated by the user in the database. RuntimeValue: It is the runtime parameter of the relevant intervention, which is returned from the database to the user. DesigntimeValue: It is the parameter of the relevant intervention, which is returned from the database to the user, describing the duration of the database design intervention. |
| SQL: Output | It is the Output data returned from the database after the database command is sent. Upload Output to Datasource: It is the Selection parameter of whether or not to save the output data obtained after the database command to the data source. Data Source: If the output data is to be saved in the data source, the Data Source parameter is the data source where these outputs will be saved. |
| SQL: Execution Result | The Records Affected parameter returned from the database after the database command is sent. Displays the numeric value of the data fields affected by the command to the user. |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Step Completion Time | The time to the end of completion for step if Run to The End of Completion of Application style is chosen. (Compulsory) |
| Wait Time After Execution Request | The wait time to pass next step. (Compulsory) |
| Parameter | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step Flow |
Indicates the step flow type. (Compulsory)
|
Performing Actions with Dynamic Data Using Command Steps
| To dynamically retrieve and update data in the process you want to develop, you can use the parameters section. The Key is the name of your variable, and RunTimeValue is the value that will be assigned to the Key variable during scenario execution. You can dynamically assign the RunTimeValue text value in three different ways: ‘Constant’, ‘Variable’, and ‘Data’. The parameter you need to use in the command step will be $P{“Key Value”}. |
#Example 1
| Key | RunTimeValue | DesignTimeValue |
|---|---|---|
| name | \datasource.1_.name\ (Value in the ‘name’ column of the data source with ID 1.) | Ahmet |
SELECT * From test where name = $P{name};
| Note! When you click the Run button, the value that will be used is DesignTimeValue, because the Run button is a test tool. During the scenario execution, RunTimeValue will be assigned to the ‘Key’ variable. |